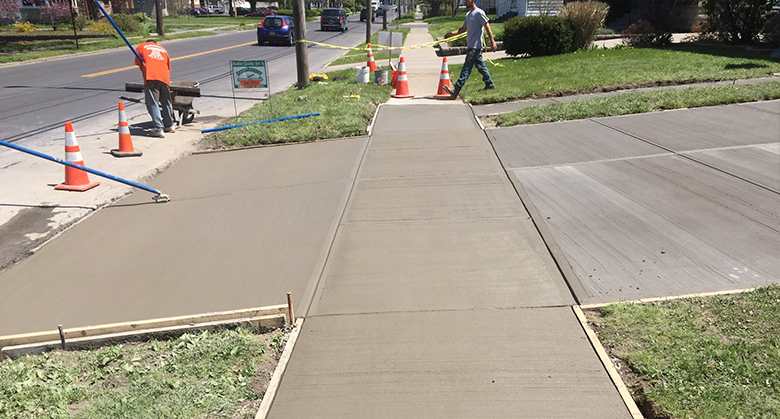
Sidewalks are an essential part of the urban landscape, providing safe pathways for pedestrians and contributing to the overall quality of life in our communities. However, like any other infrastructure, sidewalks can deteriorate over time, leading to the need for repairs. When sidewalk damage occurs, property owners often wonder whether these repairs are covered by their property insurance. we will explore the factors that determine whether sidewalk repair NYC is covered by property insurance and provide valuable insights into this common concern.
Understanding Sidewalk Responsibility
Before delving into insurance coverage, it’s crucial to understand who is responsible for sidewalk repairs. In many regions, property owners are responsible for maintaining and repairing the sidewalks adjacent to their properties. This responsibility includes addressing issues such as cracks, potholes, and damage caused by tree roots. It’s essential for property owners to be aware of local regulations and their responsibilities regarding sidewalk maintenance.
Factors That Influence Coverage
Whether sidewalk repairs are covered by property insurance can depend on several factors:
1. Type of Insurance Policy
The type of property insurance policy you have plays a significant role in determining coverage. Most standard homeowners’ insurance policies do not cover sidewalk repairs as they are typically considered the responsibility of the property owner. However, it’s essential to review your policy to understand its specific terms and limitations.
2. Cause of Damage
The cause of the sidewalk damage can impact coverage. Insurance policies often cover sudden and accidental damage, such as damage caused by a fallen tree or other unexpected events. However, gradual wear and tear or damage resulting from a lack of maintenance may not be covered.
3. Local Regulations
Local regulations and ordinances can vary significantly. Some municipalities hold property owners responsible for sidewalk repairs, while others may have programs in place to cover repair costs. Understanding the local regulations in your area is essential in determining whether you are liable for repairs.
4. Liability Issues
If sidewalk damage results in an injury to a pedestrian, liability concerns may come into play. In some cases, property insurance liability coverage may help cover legal expenses and settlement costs if you are found responsible for the injury. However, this coverage typically applies to bodily injury claims rather than sidewalk repair costs.
Insurance Coverage Options
While standard property insurance policies may not cover sidewalk repairs, property owners have a few options to consider:
1. Sidewalk Repair Coverage Endorsement
Some insurance companies offer sidewalks repair coverage endorsements or riders that can be added to your policy for an additional premium. These endorsements may provide coverage for sidewalk repairs due to sudden and accidental damage.
2. Municipal Programs
In some areas, municipalities offer programs to help property owners with sidewalk repair costs. These programs may provide financial assistance or cost-sharing arrangements for eligible repairs.
3. Liability Coverage
Property owners should also consider liability coverage within their insurance policies. This coverage can protect you in case a pedestrian is injured on your property due to sidewalk damage.
Conclusion
In most cases, standard property insurance policies do not cover sidewalk repairs, as they are typically considered the responsibility of the property owner. However, the availability of sidewalk repair coverage endorsements, municipal programs, and liability coverage provides property owners with options to consider. It’s essential to review your insurance policy, understand local regulations, and be proactive in maintaining the sidewalks adjacent to your property to prevent damage and potential liability issues. While sidewalk repairs may not always be covered by property insurance, staying informed and prepared can help property owners navigate this aspect of homeownership.