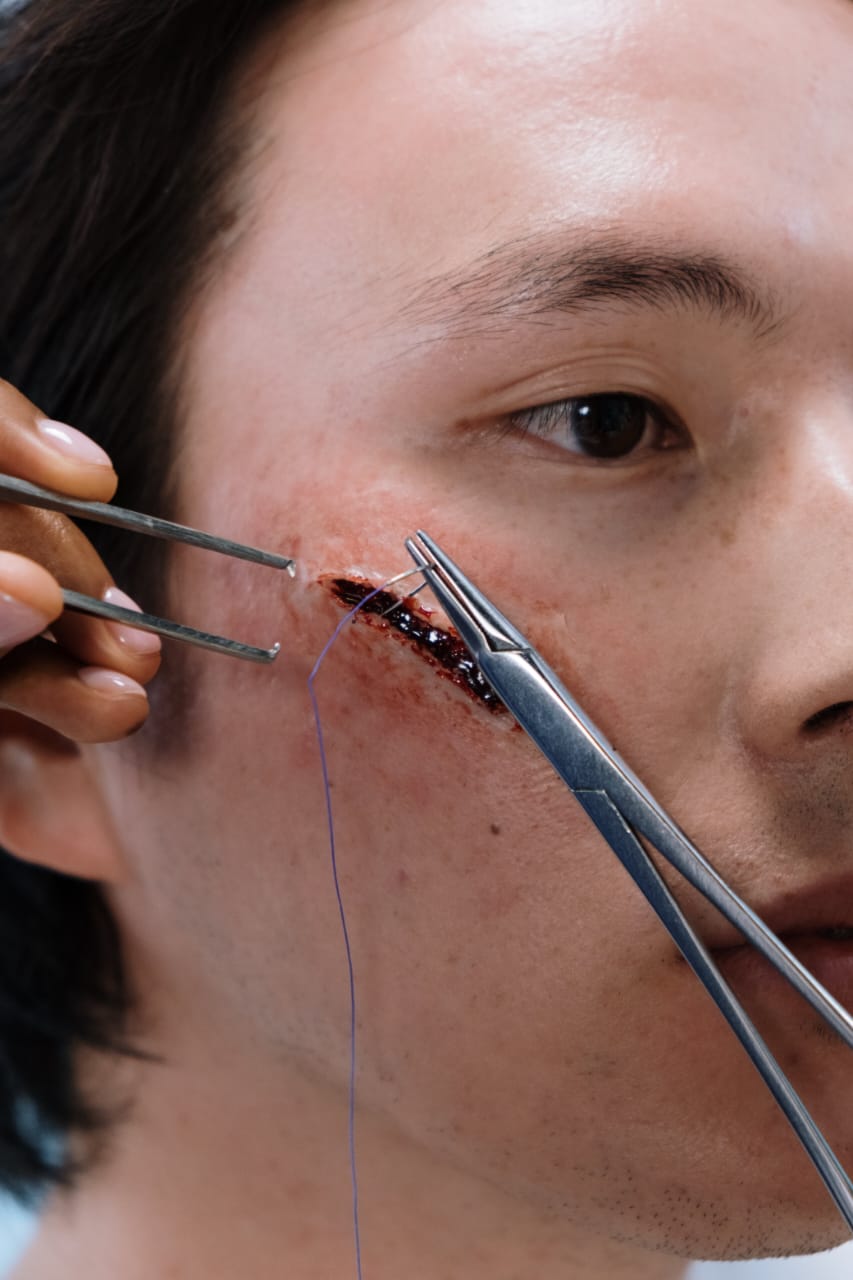
Pediatric degloved face injuries, characterized by the forcible separation of the facial skin and soft tissues from the underlying bone and muscle structure, are traumatic events with unique considerations in children. This article will delve into the causes of pediatric degloved face injuries and their management, focusing on the specific needs and challenges associated with treating young patients.
**Understanding Pediatric Degloved Face Injuries:**
Pediatric degloved face injuries are rare but severe occurrences in which the facial skin and soft tissues are abruptly separated from the underlying facial structures, exposing bones and muscles. These injuries can result from various causes:
1. **Accidental Falls:** Children are prone to falls during play or while learning to walk, which can lead to degloved face injuries when their face makes direct contact with a hard surface.
2. **Bicycle Accidents:** Bicycle accidents are common among children. A fall from a bicycle can cause facial injuries, especially if the child is not wearing a helmet or protective gear.
3. **Sports Injuries:** Young athletes participating in contact sports such as football, hockey, or rugby may be at risk of degloved face injuries due to collisions, tackles, or falls during play.
4. **Motor Vehicle Accidents:** Children can be involved in motor vehicle accidents as passengers. The impact of such accidents can lead to facial injuries if proper child safety seats or restraints are not used.
5. **Animal Bites:** In some cases, animal bites can result in facial injuries in children, causing tissue separation and trauma.
**Management of Pediatric Degloved Face Injuries:**
The management of pediatric degloved face injuries requires a comprehensive and specialized approach, considering the physical, emotional, and developmental needs of young patients. Here are key aspects of management:
1. **Immediate First Aid:** In the event of a pediatric degloved face injury, immediate first aid is essential. This includes controlling bleeding, cleaning the wound, and covering it with a sterile dressing or clean cloth. It’s crucial to avoid any further contamination.
2. **Emergency Medical Care:** Emergency medical care should be sought without delay. Children with degloved face injuries require immediate attention from healthcare professionals to assess the extent of the injury and provide appropriate treatment.
3. **Sedation and Pain Management:** Young children may require sedation or anesthesia to facilitate wound assessment and treatment. Pain management should be a priority to ensure the child’s comfort.
4. **Surgical Intervention:** Surgical repair is often necessary to reattach the facial tissues and achieve the best possible cosmetic outcome. Pediatric plastic surgeons or facial reconstructive specialists may be involved in the surgical management.
5. **Wound Cleansing and Debridement:** Thorough wound cleansing and debridement may be required to remove damaged tissue and reduce the risk of infection. This is a critical step in wound care.
6. **Tissue Reattachment:** During surgery, the separated facial tissues, including the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and muscle, are reattached and sutured carefully to restore proper alignment.
7. **Minimizing Scarring:** Minimizing scarring is a crucial aspect of management in pediatric cases. Special attention is given to suturing techniques and postoperative care to optimize cosmetic results.
8. **Emotional Support:** Pediatric patients often experience emotional distress and fear associated with their injuries and treatment. Child psychologists or counselors may be involved in providing emotional support to help children and their families cope.
9. **Developmental Considerations:** Managing pediatric degloved face injuries involves considering the child’s developmental stage and growth. Procedures should be planned to accommodate future growth and development.
10. **Rehabilitation:** After surgical repair, rehabilitation may be required to regain facial function and range of motion. This can include physical therapy and exercises to promote healing and recovery.
11. **Follow-Up Care:** Pediatric patients require thorough follow-up care to monitor healing, address any complications, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
12. **Long-Term Care:** Pediatric patients may require long-term care, including scar management and further surgical interventions as they grow.
**Conclusion:**
Pediatric degloved face injuries are challenging and require specialized care that accounts for the unique needs of young patients. Immediate first aid, emergency medical care, surgical intervention, emotional support, and rehabilitation are integral components of the management process. Providing comprehensive care while considering the child’s physical and emotional well-being is essential to achieving the best possible outcomes and supporting their long-term development and recovery.