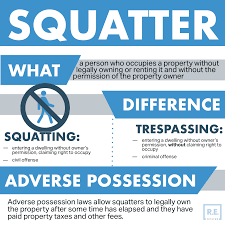
Squatters’ rights, also known as adverse possession, refer to the legal concept where someone can gain ownership of a property without the permission of the owner. This right is established through continuous, open, and unauthorized use or occupation of the property for a certain period, which varies by jurisdiction. The idea behind squatters’ rights is to prevent neglected or abandoned properties from falling into disrepair and to encourage efficient land use.
The specifics of What are squatters rights can differ significantly depending on the country and its laws. However, there are common elements in many legal systems.
One key aspect of adverse possession is the requirement of open and continuous occupation of the property. This means that the squatter must use the land openly without attempting to hide or conceal their presence. The occupation must also be continuous for a specified period, typically ranging from a few years to several decades, during which the squatter maintains uninterrupted use of the property.
Another crucial element is the intention to possess the property. The squatter must demonstrate an intention to claim ownership of the land. This intention is typically inferred from the squatter’s actions, such as making improvements, paying property taxes, or treating the land as their own.
Moreover, the concept of adverse possession often involves the absence of the true owner’s objection or action against the squatter. If the property owner is aware of the squatter’s presence but does not take legal action to remove them within a specified period, it can strengthen the squatter’s claim to the property.
Squatters’ rights can apply to various types of properties, including vacant lots, abandoned buildings, and even portions of land mistakenly believed to be part of one’s property.
However, it’s essential to note that squatters’ rights do not apply universally. There are limitations and conditions that must be met for a squatter to claim ownership. For instance, the occupation must be hostile or without the owner’s permission, and the squatter’s use of the property must be actual, exclusive, and notorious.
Additionally, laws regarding adverse possession are often complex and can vary significantly by jurisdiction. Some jurisdictions may require the squatter to fulfill specific criteria, such as payment of property taxes or making improvements to the property, to claim ownership through adverse possession.
Furthermore, squatters’ rights have their controversies and debates. Critics argue that it can incentivize trespassing and illegal occupation of properties, potentially leading to disputes and legal battles. On the other hand, proponents suggest that adverse possession laws can encourage the productive use of neglected properties and prevent land hoarding.
Overall, squatters’ rights are a complex legal concept designed to balance the interests of property owners and the efficient use of land. Understanding these rights requires careful consideration of local laws and specific circumstances, as the application of adverse possession can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another.